‘Fuel switching’ has achieved some prominence in the sustainable energy for development discourse. Fuel switching is usually used to define situations where end-users transition from less-sustainable traditional fuels, such as fossil fuels like kerosene or paraffin, or traditional woodfuels, to more sustainable sources of fuel used for the same purpose. For example, kerosene for lighting may be substituted for electric lighting from a solar home system, or woodfuels used for cooking or heating may be substituted for LPG.
Fuel switching has been particularly put forward when relating to LPG uptake in developing countries, as LPG fuel has significant benefits over other modes of fuel used for similar purposes. These can include superior combustion properties, producing less indoor air pollution with the attendant co-benefits in terms of public health. Fuel switching can lead to a reduced burden on the end-user for energy resource acquisition, such as alleviating the time burden of collecting woodfuels or purchasing charcoal/kerosene.
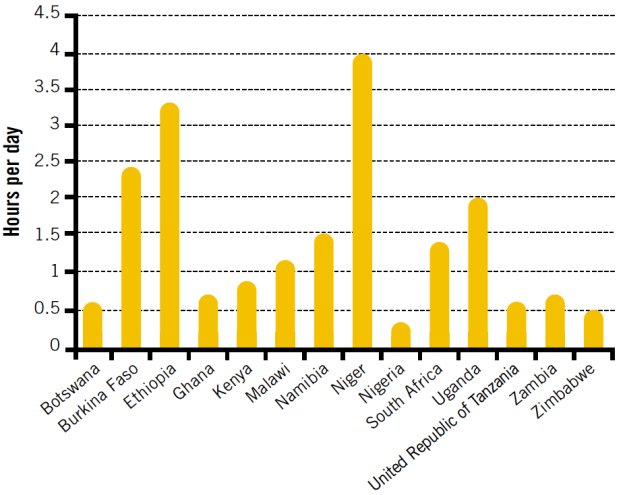
Time spent collecting wood fuels per day by women in different African countries, 1990-2003, World Bank 2006. Source: http://ourworldindata.org/data/environmental-change/indoor-air-pollution/
Fuel switching (combined with the use of efficient cookstoves) can also lead to improved performance resulting from the use of a more energy-dense fuel, such as reduced cooking times.
A comparison of different types of clean cookstoves and their relative energy consumptions and times to boil water. Source: http://www.lowtechmagazine.com/2014/06/thermal-efficiency-cooking-stoves.html
But fuel switching is not a one-way process where energy users switch to modern fuels and never come back to traditional fuels. Energy stacking is defined as when end-users in developing countries engage in multi-modal fuel usage depending on a variety of factors (e.g. variances in household income seasonally or over time), or utilising certain fuels for specific purposes (e.g. using kerosene for lighting and woodfuels for cooking).
Creating the incentive for a household, commercial enterprise or industry to engage in fuel switching can be challenging. The barriers to increased uptake of sustainable energy sources and more-sustainable energy equipment, such as solar home systems or LPG cooking apparatus, are well-documented [1] [2]. These can include higher costs for fuels, high initial investment costs putting systems/equipment out of reach of users, and problems with fuel availability, for example in distributing LPG fuels to remote rural areas.
These issues will be addressed in the next article in this series on the STEPs Blog, “Methods of Promoting LPG Uptake in Developing Countries”.
— Xavier Lemaire & Daniel Kerr, UCL Energy Institute, February 2016
[1] Pandey & Chaubal (2011) Comprehending household cooking energy choice in rural India. Biomass & Bioenergy, Vol. 35, pp. 4724 – 4731.
[2] Rai & McDonald (2009) Cookstoves and Markets – Experiences, Successes and Opportunities. Available at: http://www.hedon.info/docs/GVEP_Markets_and_Cookstoves__.pdf#